Hawaii is leading other states in generating renewable energy
08/20/2018 / By RJ Jhonson

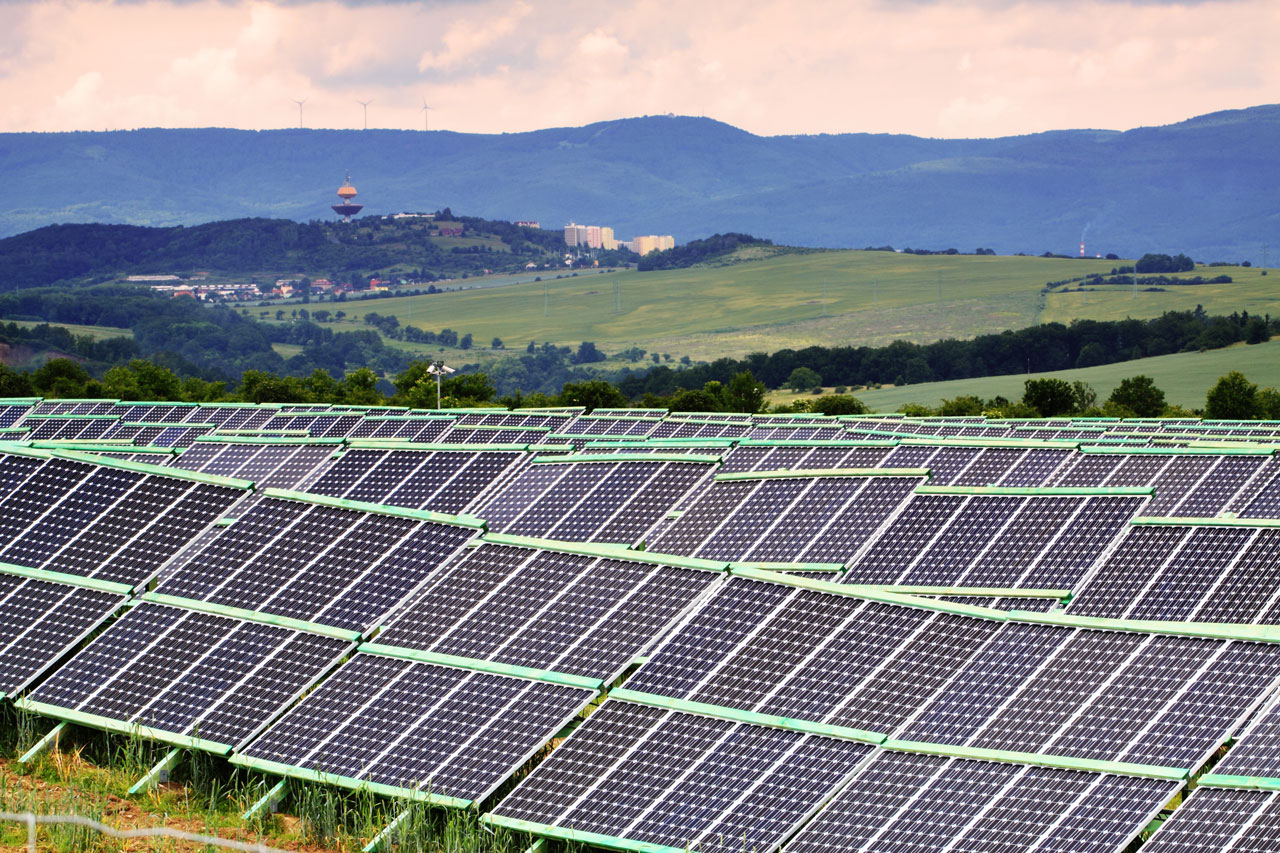
The Aloha State could be the country’s leader in renewable energy as it moves toward getting 100 percent of its power needs from both solar and wind sources by 2045.
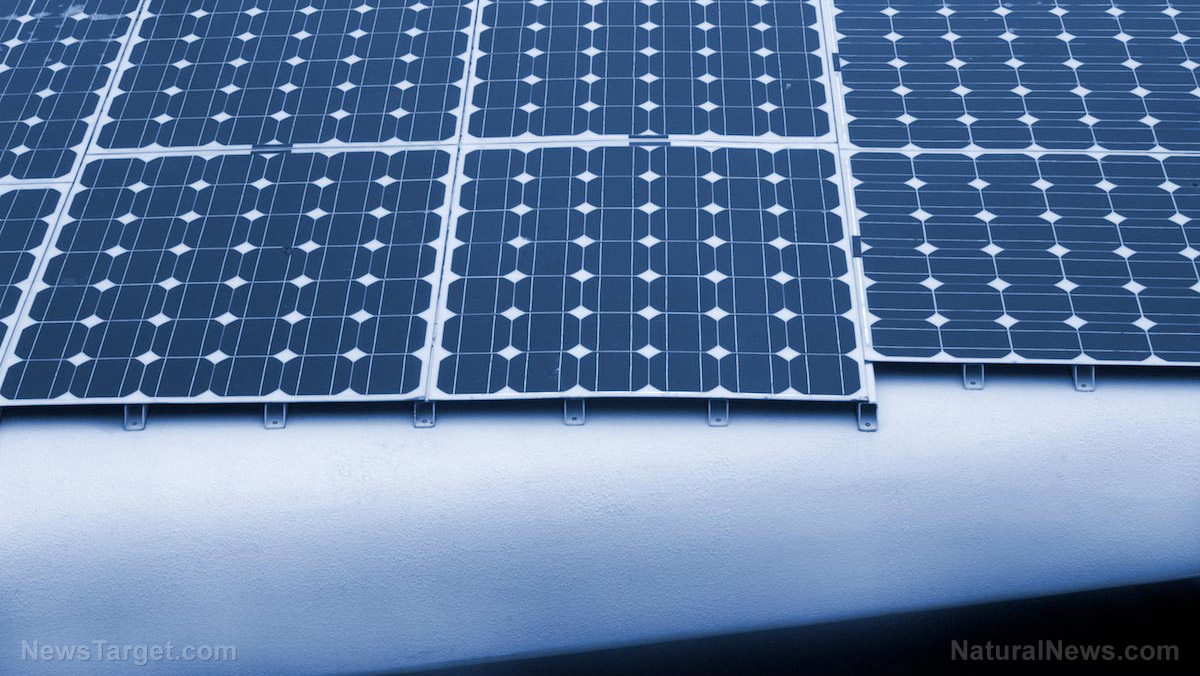
As of this year, Hawaii gets around 33 percent of its power needs from rooftop solar, although there are days when the percentage goes up to 60 percent. The move is so significant that the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) has touted Hawaii to be the “preview” that other states can do to adopt renewable energy sources.
“If this can be done in Hawaii, it can be replicated anywhere else,” Martha Symko-Davies, program manager for NREL’s Energy Systems Integration Facility said.
The enthusiasm for renewable energy is providing the state with more than just clean power. Hawaii used to get most of its power from fossil fuels, a feat for a state located in the middle of the Pacific Ocean. Solar and wind energy, being among the cheapest sources of power, are giving the state plenty of opportunities to save money.
But how does Hawaii deal with the issue of overloading, a common problem cited by naysayers of solar energy?
An article published in The Australian blamed the rapid installation of solar panels for overloading the existing power grid, potentially causing damage to devices, machines, and appliances hooked up to electric power. This has been used as one of several arguments against the move toward solar.
Hawaii’s solution to the problem is rather simple – smart inverters. These switches are designed to automatically respond to power surges, providing support for the grid and helping it handle any fluctuations.
Hawaii, however, is not alone in its bid to reduce its dependence on non-renewable energy. California, for instance, sources about 50 percent of its power needs from solar in certain days. In fact, wind and solar power now account for more than 10 percent of electricity in the U.S. This is the first time such a percentage was reached since 1984.
Furthermore, the Energy Information Administration (EIA) predicts that, for the first time in history, wind power may supplant hydroelectric power as the top source of electricity in the country this year.
Why turn to renewable energy?
Solar and wind energy are popular these days, but they are more than just mere fads. They have real and sustainable benefits that make them excellent, long-term solutions to the world’s power needs. Here are some of their other benefits:
- Less pollution – Coal and natural gas power plants are notorious for the toxins they release into the environment. Numerous studies have linked these harmful substances to various health problems, ranging from difficulties with breathing to cancer. Solar, hydroelectric, and wind power plants do not release harmful substances into the air. Geothermal and biomass plants do, but their concentrations are notably lower than what plants using fossil fuels release.
- Sustainable energy – Fossil fuel supplies are not unlimited. While estimates indicate that reserves may last for a couple of hundred years more, experts believe stepping up production could deplete coal deposits by 2088. Renewable energy relies on nature’s mainstay’s like the sun, the movement of water, strong winds, and the heat of the earth. As long as the hardware is maintained, there is very little doubt that renewable power sources will keep on giving for a long, long time.
- Economics – Fossil fuel power plants are typically mechanized, unlike plants that use renewable energy which needs people to install, repair, and maintain them on a regular basis. This means that there is more job in renewable power. There are studies noting the harmful effects of air pollution on productivity, so switching to cleaner and safer power sources will help maximize labor investments.
- Stable prices – It’s true that renewable energy requires massive investments, especially in terms of hardware. However, the cost of operating them is very low, thanks to their “fuel” being essentially free. A look at trends over the past decades indicates that the price of solar power has dropped by 70 percent between 2010 and 2017, while that of wind power decreased by 66 percent between 2009 and 2016.
Learn more about power sources and how they affect society at Power.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: biomass, Clean Energy, electricity, fossil fuel, geothermal energy, green energy, green living, Hawaii, hydroelectric power, power grid, renewable energy, solar energy, solar power, sustainable energy, sustainable living, wind energy, wind power